

Could you make it keep what's already on the screen? It would help if, say, I wanted to pull up several large molecules without recreating each from scratch. When I load a saved molecule, it deletes what I had on the screen.
CONSTRUCTING A MOLECULAR GEOMETRY TABLE FREE
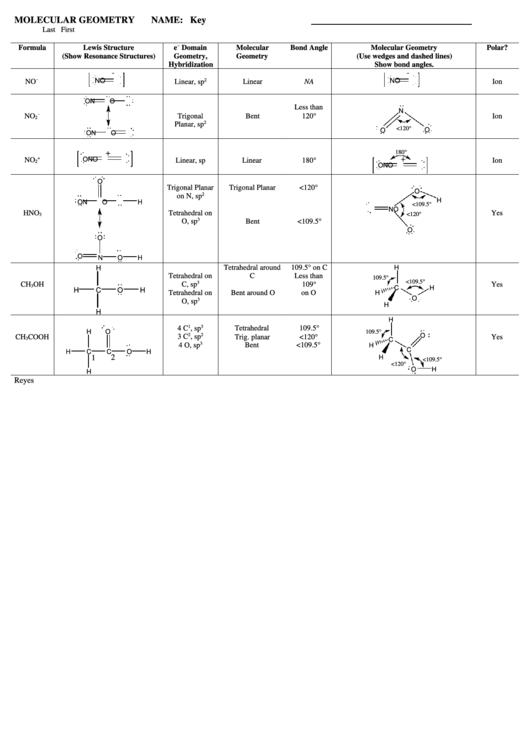
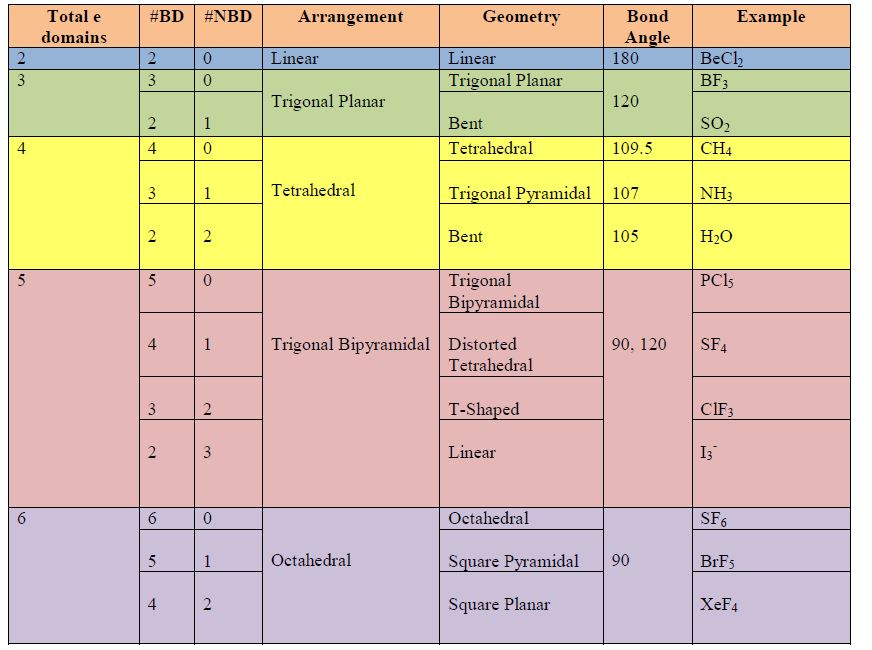
All the free apps I found were woefully insufficient, except yours!! Aaah! It has tons of atoms! I even made sucrose! Your program supports carbon rings! And VESPR theory! The molecules exhibit dipole-dipole forces when placed very close to each other! It gives data on your molecules! And you can save it! And rotate it in 3D, no glitching! Sulfur expands its octet! It's easy to use! Double and triple bonds! I can't wait to show my chemistry teacher! And clearly, you are consistently updating!Ī few things to make this app even more awesome: Without (, ) means they are different and can be counted twice.I am a high school student who wanted to do a cool visual of the dehydration of sucrose with sulfuric acid for my final. The (, ) means they are the same and can be counted once. In the same rotation there is another rotation, for instance O h has 3C 2=C 4 2 The # stands for the number irreducible representations for the sigmas. Take a look at the Lewis structures of N H 3 N H 3 and BF 3 B F 3. The # stands for the number of irreducible representation for the C n Molecular geometry is determined by the arrangement of valence electrons. Rotation of 2 π /n and then reflected in a plane perpendicular to rotation axis. Inversion of the molecule from the center Reflection of the molecule horizontally compared to the horizontal highest fold axis. While you are constructing your molecules, keep the following points in mind: Nature loves' symmetry, which means equal bond lengths and angles. Now, construct the three-dimensional geometry for the molecules listed in Table 2 on the Data Sheet. Reflection of the molecule vertically compared to the horizontal highest fold axis. Chemistry Chemistry questions and answers Part 2: Construction of Molecules 1. Reflection of the molecule perpendicular to the other sigma Symbols in the first row of the character tables Eĭescribes the degeneracy of the row (A and B= 1) (E=2) (T=3)Ģpi/n= number of turns in one circle on the main axis without changing the look of a molecule (rotation of the molecule)Ģ π /n= number of turns in one circle perpendicular to the main axis, without changing the structure of the moleculeĢ π /n= number of turns in one circle perpendicular to the C n' and the main axis, without changing the structure
On the other hand, the second method uses a projection operator on each stretching vector. The first method uses a basis set composed of the irreducible representation of the stretching modes of the molecule.
Symmetric with respect to \(σ_h\) (reflection in horizontal plane)Īnti-symmetric with respect to \(σ_h\) ( opposite reflection in horizontal plane) The SALCs of a molecule may be constructed in two ways.

Symmetric with respect to the C nprinciple axis, if no perpendicular axis, then it is with respect to σ vĪnti-symmetric with respect to the C nprinciple axis, if no perpendicular axis, then it is with respect to σ vĪnti-symmetric with respect to the inverse (thirdly degenerate or three dimensional ) (singly degenerate or one dimensional) anti-symmetric with respect to rotation of the principle axis (singly degenerate or one dimensional) symmetric with respect to rotation of the principle axis Symbols under the first column of the character tables A (Mulliken Symbol) The character tables takes the point group and represents all of the symmetry that the molecule has. \)Įvery molecule has a point group associated with it, which are assigned by a set for rules (explained by Group theory).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
